SMS code login
Password Login
Get SMS verification code
Bearing original clearance and working clearance
2023-03-27
Whether a rolling bearing can perform its normal function largely depends on whether it can achieve the appropriate working clearance. The working clearance is determined by the tolerance fit selected for the original radial clearance before installation and the effect of temperature
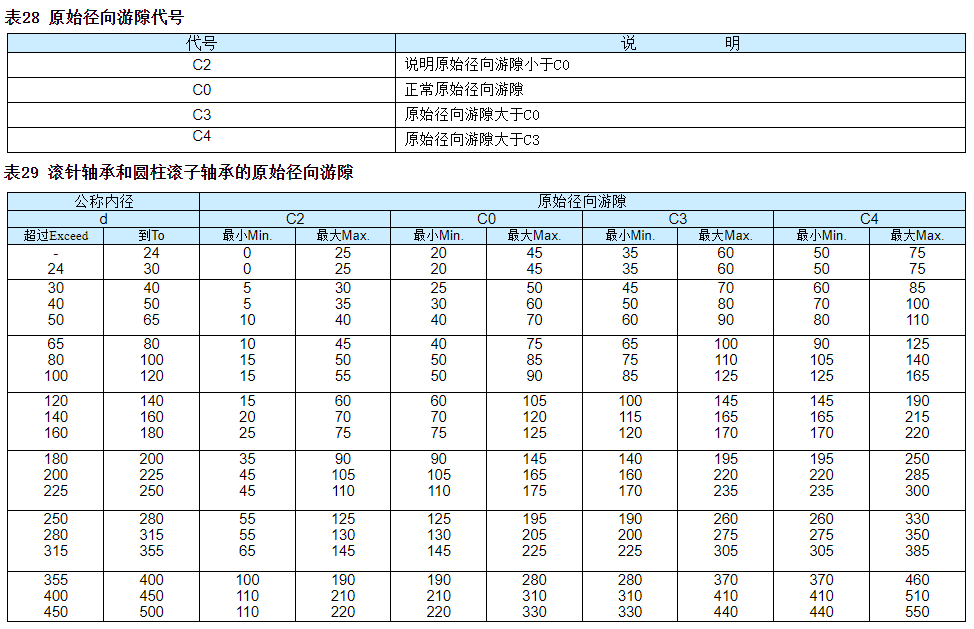
Original radial clearance
The original radial clearance of a rolling bearing is the amount of radial movement of the inner ring relative to the outer ring from one extreme position to the other without radial force before installation
The normal original radial clearance C0 of RTL needle roller bearings and cylindrical roller bearings is selected based on the technical notes at the front of the dimension table or the previously recommended tolerance limits for shafts and bearing housings, as well as the working clearance that can achieve normal function under normal operating conditions
Under other assembly and operating conditions, such as interference fit of bearing rings, special bearing temperatures, etc., the required original radial clearance of the bearing is different from the normal clearance. Radial bearings with original radial clearance different from normal clearance can be identified using the supplementary codes listed in Table 28
This supplementary code (except C0) is added to the bearing code or combined with the accuracy level supplementary code
The values for each group of bearing clearance are given in Table 29. The tolerance zone for the inner circle diameter of needle roller bearings without inner rings provided by RTL is F6
The original radial clearance of C2 is only used in very special situations, such as heavy alternating loads and low speed operation or swing situations. In this case, significant heat generation is expected, so it is recommended that the bearings be monitored during bearing operation
The original radial clearance of bearings C3 and C4 are used in situations where interference fits are selected for the rings or when the temperature gradient between the inner and outer rings is large, especially when using large bearings
Working Clearance
The working clearance of a bearing is defined as the amount of radial movement of the shaft relative to the outer ring of the bearing under no load after installation. The working clearance is the original radial clearance minus the amount of clearance change caused by interference fit and thermal expansionΔ S (inμ m units)
ΔS=ΔSP ΔST .............................(44)
Clearance reduction due to interference fitΔ SP can be calculated by formula (45), the clearance reduction due to thermal expansionΔ ST can be calculated by formula (46). When using formula (46), pay attention to its positive and negative signs
Normal working clearance
If, under normal working load conditions, bearings with inner rings are matched with bearing pedestals and shafts with the tolerance zones specified in Tables 14 and 15, or if bearings without inner rings are selected with shafts with the tolerance zones specified in Table 16, bearings with an original radial clearance of C0 can generally obtain normal working clearance
Working clearance smaller than normal working clearance
For rolling bearings, small working clearance can only be used for special occasions, such as precision machine tools, measuring instruments and equipment, or occasions with alternating loads
Working clearance larger than normal working clearance
Bearings with large working clearance are mainly used in situations of relative inclination and shaft bending
The impact of cooperation on work clearance
Original radial clearance reduction due to interference fitΔ SP (μ m) is due to inner ring expansionΔ D and outer ring shrinkageΔ Caused by D
ΔSP=Δd ΔD ...............................(45)
According to experience, there are two ways to theoretically determine the interference amount of a mating part: one is to take its average deviation, and the other is to take the deviation limit value close to the machining surface, plus or minus one-third of the tolerance zone value. The value of the mutual flattening of surfaces during assembly must be subtracted. The average value of the dimensional change can be found in Table 30
For thin-walled bearing blocks and light metal bearing blocks, the effective interference cannot be reliably calculated; In this case, it is recommended that the reduction in the original radial clearance be determined by installation testing
Effect of temperature on working clearance
When there is a large temperature gradient between the inner and outer rings of the bearing, there will be considerable changes in the working clearance of the bearing. This can sometimes affect the normal function of the bearing. If the thermal expansion coefficient of steel isα= 0.000011 (K-1), the temperature difference between the inner and outer rings is&Delta, Then the radial clearance variation isΔ ST (μ m) is:
ΔST≈0.11.dM.Δ .........................(46)
Temperature difference between inner and outer ringsΔ It is possible to reduce or increase the working clearance, so using theΔ You must pay attention to its positive and negative signs. If the inner ring temperature is higher than the outer ring temperature,Δ Take a positive value. If the outer ring temperature is higher than the inner ring temperature,Δ A negative value should be taken


